
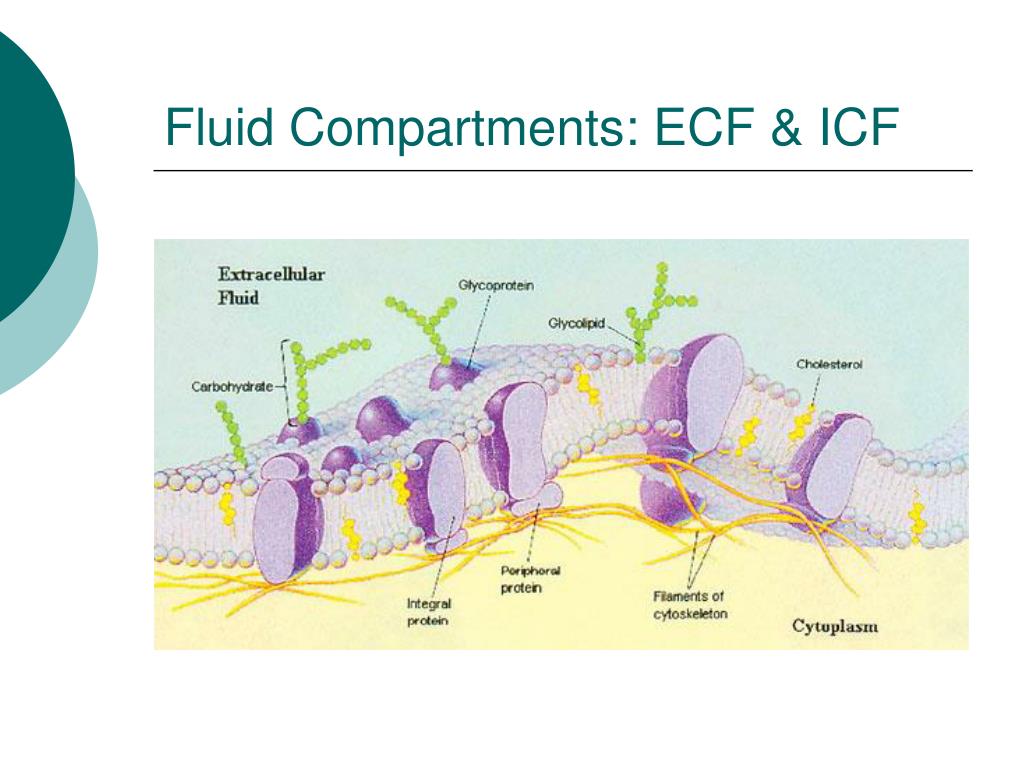
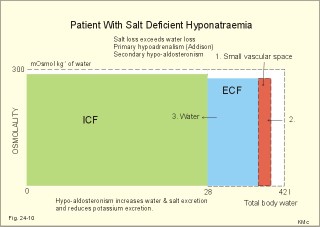
Due to hydromechanics, the method is distinct from previously described techniques for CSF withdrawal. Here, I describe the surgical procedure for efficient and reproducible access and injection of therapeutic agents such as stem cells to cisterna magna. The cisterna magna is the largest CSF fluid compartment thus it was selected as a target. In small animals access to CSF is not trivial. The tight junctions are narrow belts that circumferentially surround the upper part of the lateral surfaces of the adjacent epithelial cells to create fusion points or 'kisses'. It is warranted by the direct delivery of therapeutic agents beyond the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and widespread access to the large areas of the brain and the spinal cord. Three distinct regions are characterized: the cellular interior (intracellular fluid), the medium between. Finally, I describe the method for CNS dissection within intact dura for evaluation of cell distribution.ĪB - The CSF is increasingly considered as an attractive gateway to the central nervous system (CNS). Figure 1: Ionic composition in mammalian organisms. In all cases the major constituent is water derived from the environment. The intracellular component includes the body cells and, where present, the blood cells, while the extracellular component includes the tissue fluid, coelomic fluid, and blood plasma. Due to hydromechanics, the method is distinct from previously described techniques for CSF withdrawal. The fluid compartments of animals consist of intracellular and extracellular components. In small animals access to CSF is not trivial. N2 - The CSF is increasingly considered as an attractive gateway to the central nervous system (CNS).
T1 - Surgical access to cisterna magna using concorde-like position for cell transplantation in mice and CNS dissection within intact dura for evaluation of cell distribution


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
